The skin between the toes is often susceptible to fungal infections. This problem often occurs in people who lead an active lifestyle and is quite stressful and unpleasant. Given the high relevance of mycoses on the feet, increased attention should be paid to them.
Causes of itching and peeling in the interdigital folds
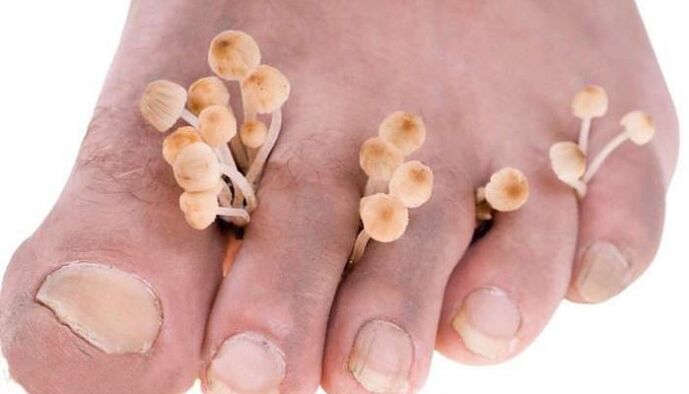
Toes itch and peel due to various pathological processes - allergic reactions, scabies, eczema - but in many people such symptoms arise from a fungal infection. The epithelium becomes wet and tears during mycosis of the feet, which is a separate nosology in dermatology. It is caused by pathogenic fungi that affect smooth skin and nail plates. The infection is caused by several pathogens:
- Trichophyton (T. rubrum, T. interdigitale, T. violaceum).
- Epidermophyton (E. floccosum).
- Molds.
Mycosis is a contagious disease that is transmitted from one person to another through infected shoes, carpets, benches, etc. in places with high humidity (spas, saunas, swimming pools, beaches). Fungal spores occur in large quantities in the horny scales of the epidermis, with which and are transmitted.
Predisposing factors
A number of local and general factors contribute to skin lesions and increase the likelihood of a fungal infection between the fingers. The first include the following:
- Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis).
- Incorrectly selected shoes (uncomfortable, made of synthetic materials).
- Anatomical features of the foot (flat feet, narrow folds).
- Presence of abrasions and diaper rash.
- Injuries (mechanical, chemical).
The role of systemic disorders is explained by a decrease in the resistance of the skin barrier and a weakening of immune defenses. Neurotrophic, vascular and endocrine metabolic diseases (polyneuropathy, angiopathy, arteriosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, hypovitaminosis) have a negative effect. In addition, the role of meteorological conditions (high temperature and humidity) and the virulence of the pathogen is highlighted.
Mycosis of the foot with skin lesions between the toes is caused by a fungus and develops against the background of local or systemic disorders.
What does mycosis look like?
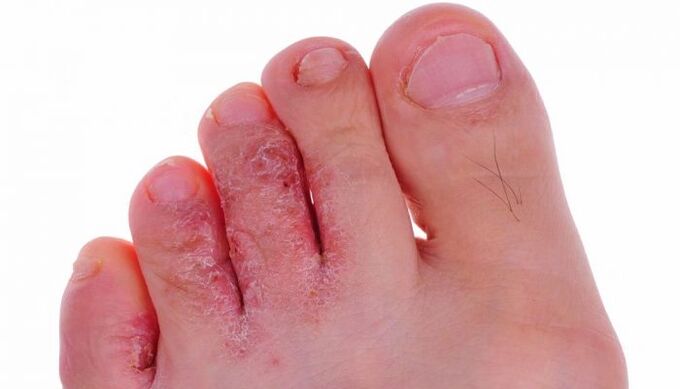
Mycosis begins in the skin of the interdigital folds, but then spreads to other parts of the foot - the sole, back and lateral surfaces. In clinical practice there are different forms of fungal infections:
- Squamous cell carcinoma.
- Intertriginous.
- Dyshidrotic.
The scaly form begins with slight redness and slight flaking. They can be limited to only certain areas or they can spread widely. This form often goes unnoticed by the patient and is therefore epidemiologically the most dangerous. The fungus initially affects one foot, but later it can also spread to the healthy side.
As the course progresses, the squamous cell carcinoma form can transform into a dyshidrotic form, which is characterized by an acute course with allergies of the body and blistering on the arch of the foot. They merge and form multi-chambered blisters which, when opened, leave eroded foci surrounded by a rim of exfoliated epidermis. The process spreads to the lateral surfaces of the foot and joins the intertriginous form. As epithelialization occurs, the areas dry out and turn back into squamous cell carcinoma.
Foci of fungal infection are often accompanied by itching. It comes from the interdigital folds in the most common form – intertriginous, which occurs independently or against the background of squamous cell carcinoma. Usually the process begins between the IV and V toes (less often III and IV). Cracks appear there, surrounded by a rim of exfoliated epidermis. The fungus can spread to other wrinkles, fingers and the back of the foot. Tears later occur with painful erosions.
The disease is characterized by a long course with periodic exacerbations that occur in the warm season. The bacterial flora penetrates more easily through the loosened stratum corneum of the epidermis, so the intertriginous form can be complicated by streptococcal infection with the development of erysipelas and thrombophlebitis.
Damage to the interdigital spaces often occurs in combination with other forms of foot mycosis, which indicates the unity of pathological processes.
diagnosis
The disease has a rather characteristic clinical picture, therefore the initial diagnosis is made based on the results of a medical examination. To identify the pathogen, microscopy and culture of abrasions of the affected skin are used. The presence of a systemic pathology that contributes to the development of mycosis is confirmed by additional methods - a biochemical blood test (glucose, hormonal spectrum, immunogram), ultrasound examination of the lower extremities, etc.
How do you treat the wound?

To effectively get rid of the fungus, you must first eliminate the conditions that create favorable conditions for its development. If your foot is itchy and sore, it is recommended to follow the following recommendations:
- Wear comfortable, breathable shoes.
- Wear cotton socks.
- Dry your feet after showering and bathing.
- Use personal slippers in public places.
In the treatment of foot mycoses, attention is paid to giving up bad habits, a healthy diet (reducing animal fats, sweets, including fresh vegetables, fruits, lactic acid products in the diet) and hardening.
In addition to general recommendations with a therapeutic and prophylactic focus, conventional medicine actively uses means of drug correction, without which a cure for mycoses is not possible. Therapy can be external or systemic.
Effective creams and ointments
It is necessary to fight the infection with specific medications that work against fungus on the toes. In the case of squamous cell carcinoma, the doctor prescribes various creams and ointments, which also include various antifungals. If there are dense foci of hyperkeratosis on the soles of the feet, treatment begins with peeling procedures with salicylic acid, lactic acid, resorcinol and collodion. A medicine intended for external use is placed under the bandage at night. It contains salicylic acid, which has anti-inflammatory, keratolytic and antiseptic properties, and in the morning take a soap and soda bath, after which the horny masses are better removed.
When your skin gets wet and cracks

External treatment of the dyshidrotic form with oozing and cracks begins with lotions containing boric acid and potassium permanganate. The interdigital spaces are treated with solutions of aniline dyes, a product for external use used to treat various skin diseases. The solution contains components that promote rapid wound healing, eliminate inflammatory phenomena and fight pathogenic microorganisms. After eliminating the acute inflammatory process, antifungal ointments and pastes are applied to the affected areas. With secondary pyoderma, drugs with antibacterial components are prescribed.
In the case of mycotic lesions of the skin of the feet, external therapy with antifungal agents, antiseptics and antibiotics is of crucial importance.
pills
If local remedies are ineffective, it is necessary to switch to medications for internal use. Antifungal medications prescribed include an antimycotic, a broad spectrum antifungal against fungi that cause diseases of the skin, hair, and nails, a medication used to treat fungal infections, and an antifungal. If the body is allergic, antihistamines (an antihistamine used to treat allergic reactions) and desensitizing agents (calcium gluconate, sodium thiosulfate, magnesium sulfate) are used. Streptococcal infections can be cured with antibiotics that do not have an activating effect on the microbial flora.
What can you do with folk remedies?
Some methods of traditional medicine can be an adjunct to standard therapy. To treat athlete's foot, baths with simple and inexpensive means are often used:
- apple cider vinegar (1 glass per 3 liters of hot water) and soda (5 tbsp).
- Potassium permanganate (1 g per 2 l).
- Decoction of marigold flowers (250 g per 2 l).
It is recommended to soak your feet in the prepared solution for 20 minutes. Additionally, you can apply a drop of tea tree essential oil to the skin between your toes and then put on cotton socks.
Fungus between toes is a problem that affects many people. To get rid of it as quickly as possible, you should not look for possible solutions on your own, but rather consult a doctor, undergo a diagnosis and receive treatment with a guaranteed result.